
Why single-phase induction motor is not a self-starting?
We can easily conclude that the single-phase induction motors are not self-starting because the produced stator flux is alternating in nature and at the starting, the two components of this flux cancel each other, and hence there is no net torque.
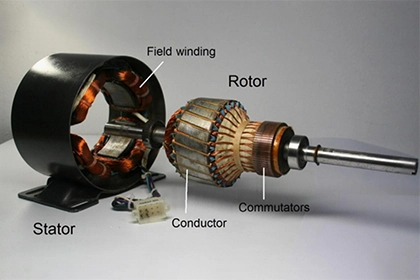
A single-phase induction motor is an AC motor that is powered by a single-phase power supply. Unlike its three-phase counterpart, a single-phase induction motor is not self-starting. This means that it requires an external means of starting rotation before it can produce torque and drive a load.
The reason for this is that a single-phase induction motor relies on the interaction between the stator winding and the rotor winding to produce torque. The stator winding is connected to the single-phase power supply and creates a rotating magnetic field. The rotor winding, which is located inside the stator, also has a magnetic field. The interaction between these two fields creates a torque that causes the rotor to rotate. However, when the motor is first started, there is no initial rotation of the rotor. This means that there is no interaction between the stator and rotor fields, and therefore no torque is produced. To overcome this problem, an external means of starting rotation is required.
Method for self-starting of single-phase motor
- There are several methods that can be used to start a single-phase induction motor . One common method is the use of a starting capacitor. This capacitor is used to create a phase shift between the current in the stator winding and the rotor winding, which produces a torque that causes the rotor to rotate.
- Another common method is the use of a starting winding, which is a separate winding that is used to create a rotating field in the motor. Once the motor is running, the starting winding is disconnected, and the motor operates as a normal single-phase induction motor.
Conclusion
Single-phase induction motor is not self-starting due to the lack of interaction between stator and rotor winding magnetic field when the motor is first started, which leads to no torque being produced. To overcome this problem, an external means of starting rotation is required, such as starting capacitor or starting winding.


Leave a Comment