
What is the difference between AC and DC electric motors?
AC electric motors are powered by alternating current, while DC electric motors are powered by direct current. AC motors are generally more complex and suitable for high-power applications, while DC motors are simpler and efficient for low-power applications.
The electric motor industry has made tremendous progress since the motor was invented. Today, electric motors are ubiquitous and used in a wide range of applications, from small household appliances to large industrial machines. In this chapter, we will delve into the differences between AC and DC motors to help you understand them better.
Types of AC motors
The two main types of AC motors are induction motors and synchronous motors. Induction motors are further divided into two types: single-phase and three-phase. Single-phase induction motors are typically used for small appliances, while three-phase induction motors are the workhorse for industrial applications, driving pumps, fans, and conveyors.
Synchronous motors are typically used in applications that require constant speed under varying load conditions, such as generators, fans, and pumps.
Types of DC motors
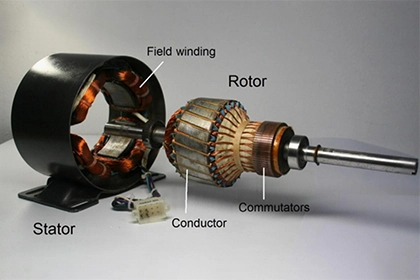
DC Motors run on direct current and are commonly used in applications that require precise speed and torque control. The two main types of DC motors are brushed motors and brushless motors.
The main differences between AC and DC motors
- Current type: AC motors run on AC, while DC motors run on DC. Efficiency: AC induction motors are usually less efficient than DC motors, especially at low speeds. Brushless DC motors are known for their high efficiency.
- Maintenance: AC motors, especially induction motors, have fewer moving parts and require less maintenance than brushed DC motors.
- Applications: AC motors dominate industrial applications, while DC motors are the preferred choice for precise speed and torque control in applications such as electric vehicles and robotics.
Conclusion
AC motors and DC motors differ in motor type, power supply, efficiency, and maintenance. Understanding these differences is critical to selecting the right motor. As new technologies continue to emerge and evolve, the capabilities and applications of AC and DC motors are likely to expand, further cementing their importance in the motor industry.


Leave a Comment