
What is cogging in induction motor?
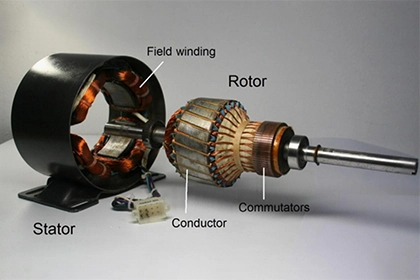
Cogging in an induction motor is the phenomenon where the motor experiences a reluctance torque due to the interaction between the rotor and stator teeth. This can cause the motor to vibrate or make noise and can reduce its efficiency and performance.
Cogging is a phenomenon that occurs in induction motors when the rotor and stator windings are not perfectly aligned. This causes the rotor to produce small pulses of torque as it rotates, resulting in a jerky or pulsing motion. Cogging is a common problem in induction motors and can reduce their efficiency and performance. In this article, we will explain what cogging is and how it can be prevented or mitigated.
Cogging is caused by the interaction between the rotor and stator windings of an induction motor. When the rotor and stator windings are not perfectly aligned, the rotor produces small pulses of torque as it rotates. This results in a jerky or pulsing motion, which is known as cogging. Cogging can be caused by a variety of factors, including manufacturing defects, misalignment of the rotor and stator, and incorrect winding patterns.
There are several ways to prevent or mitigate cogging in induction motors. The most effective method is to use a rotor with a smooth, uniform surface and carefully align the rotor and stator windings. This can help to minimize the interaction between the rotor and stator windings and reduce the occurrence of cogging. Other methods include using a rotor with a larger diameter, using a higher-quality electrical power supply, and increasing the number of stator windings.
In conclusion, cogging is a phenomenon that occurs in induction motors when the rotor and stator windings are not perfectly aligned. It can cause the motor to produce a jerky or pulsing motion, which can reduce its efficiency and performance. By using a rotor with a smooth, uniform surface and carefully aligning the rotor and stator windings, you can prevent or mitigate cogging and ensure optimal performance and efficiency.
Cogging is a phenomenon that occurs in induction motors when the rotor and stator windings are not perfectly aligned. This causes the rotor to produce small pulses of torque as it rotates, resulting in a jerky or pulsing motion. Cogging is a common problem in induction motors and can reduce their efficiency and performance. In this article, we will explain what cogging is and how it can be prevented or mitigated.
Cogging is caused by the interaction between the rotor and stator windings of an induction motor. When the rotor and stator windings are not perfectly aligned, the rotor produces small pulses of torque as it rotates. This results in a jerky or pulsing motion, which is known as cogging. Cogging can be caused by a variety of factors, including manufacturing defects, misalignment of the rotor and stator, and incorrect winding patterns.
There are several ways to prevent or mitigate cogging in induction motors. The most effective method is to use a rotor with a smooth, uniform surface and carefully align the rotor and stator windings. This can help to minimize the interaction between the rotor and stator windings and reduce the occurrence of cogging. Other methods include using a rotor with a larger diameter, using a higher-quality electrical power supply, and increasing the number of stator windings.
In conclusion, cogging is a phenomenon that occurs in induction motors when the rotor and stator windings are not perfectly aligned. It can cause the motor to produce a jerky or pulsing motion, which can reduce its efficiency and performance. By using a rotor with a smooth, uniform surface and carefully aligning the rotor and stator windings, you can prevent or mitigate cogging and ensure optimal performance and efficiency.


Leave a Comment