
What does induction motors do?
An induction motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy to power machinery and equipment. It works based on electromagnetic induction and the rotating magnetic field created by the stator.
An induction motor is a type of electric motor that uses electromagnetic induction to generate rotational motion. This type of motor is widely used in a variety of applications, including fans, pumps, compressors, conveyors, and many other machines that require a rotational motion.
To understand what an induction motor does, it is helpful to consider the basic operating principle of this type of motor. An induction motor uses electromagnetic induction to generate rotational motion, which is accomplished by creating a magnetic field around a coil of wire.
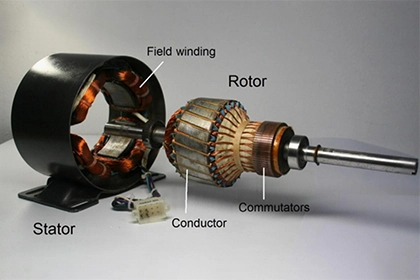
In an induction motor, the magnetic field is produced by the stator, which is a stationary component that consists of a series of copper or aluminum coils. The stator is typically mounted on the outer shell of the motor, and it is connected to the electrical power supply. When an electrical current flows through the stator coils, it creates a magnetic field that extends into the rotor, which is a moving component that is mounted on the motor's shaft.
The rotor is typically made up of a series of conductive bars that are connected to a series of short-circuited end rings. When the rotor is placed in the magnetic field produced by the stator, it experiences a force known as the "rotor reaction," which causes it to rotate. This rotational motion is transferred to the motor's shaft, which can then be used to drive a load.
The key to the operation of an induction motor is the interaction between the magnetic fields of the stator and rotor. When the stator's magnetic field rotates, it creates a current in the rotor's conductive bars, which in turn creates its own magnetic field. This magnetic field interacts with the stator's magnetic field, resulting in a force that causes the rotor to rotate.
The rotational motion of the induction motor is typically used to drive a load, such as a fan, pump, compressor, or conveyor. The speed and torque of the induction motor can be controlled by varying the voltage, frequency, and number of phases of the electrical power supply.
One of the key advantages of an induction motor is its efficiency and reliability. An induction motor can operate efficiently over a wide range of speeds and loads, and it can be easily controlled and maintained. In addition, an induction motor does not require any mechanical commutation, as the stator's magnetic field drives the rotor's magnetic field and the rotor itself. This eliminates the need for brushes, which reduces the maintenance requirements of the motor.
Another advantage of an induction motor is its versatility. An induction motor can be easily adapted to different applications by changing the size, number of poles, and configuration of the stator and rotor. This allows the induction motor to be used in a wide range of applications, including fans, pumps, compressors, conveyors, and many other machines that require a rotational motion.
In summary, an induction motor is a type of electric motor that uses electromagnetic induction to generate a rotating magnetic field, which in turn, produces torque and rotates the motor shaft. It is widely used in various industrial and commercial applications due to its simplicity, reliability, and low maintenance requirements.


Leave a Comment