
How does induction motor starts?
As the name suggests, the induction motor is started by connecting it directly to three-phase supply. In this method, the motor draws a high starting current (about 4 to 7 times of the rated current) and at low power factor. Therefore, DOL starting is suitable for relatively small motors (up to 10 kW).
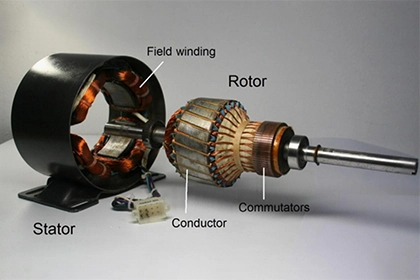
An induction motor is a type of electric motor that operates based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. Induction motors are commonly used in industrial and residential applications due to their simple construction, low cost, and high reliability. In this article, we will discuss the process of how an induction motor starts and how it works.
Starting an Induction Motor Starting an induction motor requires the application of an initial rotational force to the rotor, which is required to generate the initial magnetic field. This rotational force is typically provided by a secondary motor or by a series of capacitors connected in parallel with the motor winding.
The starting process begins by applying a starting voltage to the motor winding. This causes a current to flow in the winding, which generates a magnetic field. The interaction between the magnetic field and the magnetic field generated by the stator winding induces a current in the rotor winding. This current generates a magnetic field in the rotor, which interacts with the magnetic field generated by the stator.
The interaction between the magnetic field generated by the stator and the magnetic field generated by the rotor creates a torque, which causes the rotor to rotate. As the rotor rotates, its magnetic field moves past the stator winding, inducing a current in the rotor winding. This current generates a magnetic field in the rotor, which reinforces the magnetic field generated by the stator, causing the rotor to continue to rotate.
Working Principle of an Induction Motor Once the induction motor is started, it operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction. The stator winding is supplied with alternating current (AC), which generates a rotating magnetic field. The rotating magnetic field induces a current in the rotor winding, which generates a magnetic field in the rotor. The interaction between the magnetic field generated by the stator and the magnetic field generated by the rotor creates a torque, which causes the rotor to rotate.
The speed of the rotor is dependent on the frequency of the alternating current supplied to the stator winding. The difference between the speed of the stator magnetic field and the speed of the rotor is known as the slip, which determines the torque produced by the motor. The torque produced by the motor is proportional to the slip, with a higher slip resulting in a higher torque.
Conclusion Induction motors are widely used in industrial and residential applications due to their simple construction, low cost, and high reliability. The starting process of an induction motor involves the application of an initial rotational force to the rotor, which is required to generate the initial magnetic field. Once started, the motor operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, with the interaction between the magnetic field generated by the stator and the magnetic field generated by the rotor creating a torque, which causes the rotor to rotate. Understanding the working principle of an induction motor is essential for selecting and maintaining this type of motor.


Leave a Comment