
How Does an AC Gear Motor Work?
In this article, we will explore how AC gear motors work, their components, and their applications in different industries.
AC gear motors are a type of motor that combines an AC (alternating current) motor with a gear system. This combination allows for efficient and controlled movement in various applications. In this article, we will explore how AC gear motors work, their components, and their applications in different industries.
Understanding AC Motors
Before delving into AC gear motors, it's important to have a basic understanding of AC motors. AC motors are electric motors that run on alternating current. They are widely used in various applications due to their simplicity, reliability, and ease of use.
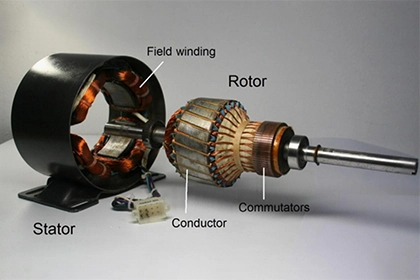
AC motors consist of two main components: a stator and a rotor. The stator is the stationary part of the motor and contains the winding coils. The rotor is the rotating part that interacts with the magnetic field generated by the stator. When an AC voltage is applied to the stator, it creates a rotating magnetic field, which in turn causes the rotor to rotate.
Introduction to Gear Systems
Gear systems are mechanisms that transmit and control power between rotating shafts. They consist of two or more gears that interlock and transfer torque from one shaft to another. Gears are toothed wheels that mesh together, allowing for the transfer of rotational motion and torque.
Gear systems provide several advantages, including speed reduction or increase, torque multiplication, and directional control. They are commonly used in applications where precise control over speed and torque is required.
How AC Gear Motors Work
AC gear motors combine the principles of AC motors and gear systems to provide controlled and efficient movement. The gear system is typically integrated into the motor assembly, with the output shaft of the motor directly connected to the input shaft of the gear system.
The gear system in an AC gear motor consists of multiple gears with different sizes, known as the input gear and the output gear. The input gear is connected to the motor's output shaft, while the output gear is connected to the load or the driven mechanism.
When the AC motor is powered, it rotates the input gear. The teeth on the input gear mesh with the teeth on the output gear, transferring rotational motion from the motor to the output gear. The gear ratio, determined by the sizes of the input and output gears, determines the speed and torque output of the AC gear motor.
The gear system in an AC gear motor allows for speed reduction or increase, depending on the gear ratio. For example, if the output gear has fewer teeth than the input gear, the output shaft will rotate at a slower speed but with increased torque. Conversely, if the output gear has more teeth than the input gear, the output shaft will rotate at a faster speed but with decreased torque.
Components of AC Gear Motors
AC gear motors consist of several key components that work together to provide controlled and efficient movement. These components include:
-
Stator: The stator is the stationary part of the AC motor and contains the winding coils that generate the rotating magnetic field.
-
Rotor: The rotor is the rotating part of the AC motor that interacts with the magnetic field generated by the stator.
-
Gear System: The gear system consists of multiple gears that transmit and control power between the motor and the load. It includes the input gear, output gear, and any intermediate gears.
-
Housing: The housing encloses and protects the internal components of the AC gear motor.
-
Bearings: Bearings support the rotating shafts of the motor and reduce friction for smooth operation.
-
Output Shaft: The output shaft is connected to the output gear and transfers rotational motion to the load or driven mechanism.
Applications of AC Gear Motors
AC gear motor find applications in a wide range of industries and equipment where controlled and efficient movement is required. Some common applications include:
-
Robotics: AC gear motors are commonly used in robotic systems to control the movement of robot arms, joints, and other mechanical components.
-
Conveyors: AC gear motors are used in conveyor systems to move materials efficiently and precisely.
-
Industrial Machinery: AC gear motors are employed in various industrial machinery, such as packaging machines, printing presses, and CNC machines, to provide controlled motion and speed adjustment.
-
Automotive Industry: AC gear motors are used in automotive applications, such as power windows, windshield wipers, and seat adjustments.
-
HVAC Systems: AC gear motors are utilized in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems for controlling dampers, fans, and valve movements.
-
Medical Equipment: AC gear motors are found in medical devices, such as surgical robots, infusion pumps, and diagnostic equipment, for precise and controlled movements.
In conclusion, AC gear motors combine the principles of AC motors and gear systems to provide controlled and efficient movement in various applications. By integrating a gear system into an AC motor, these motors offer speed reduction or increase, torque multiplication, and precise control over movement. With their versatility and reliability, AC gear motors play a vital role in industries ranging from robotics to automotive and are essential for achieving precise and efficient motion in a wide array of applications.


Leave a Comment